Fungal nail Infections
In Conditions
Follow this topic
Bookmark
Record learning outcomes
Nails damaged by a fungal infection can be a cause of considerable discomfort and embarrassment. Christine Clark PhD, FRPharmS looks at what can be done to relieve the condition
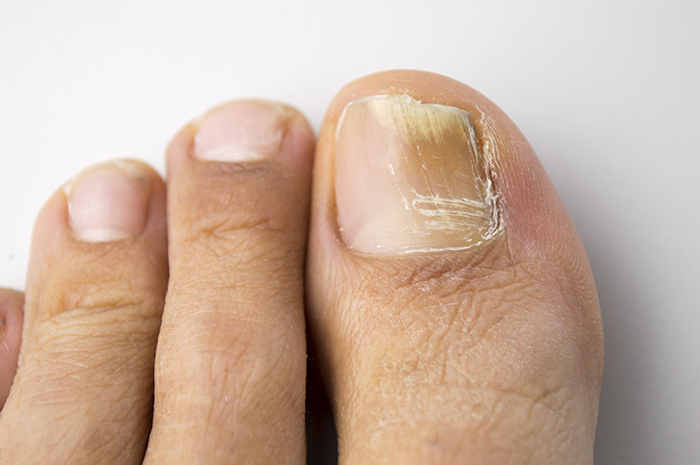
As well as causing embarrassment, a fungal nail infection can be painful and sufferers can have difficulty finding comfortable shoes. In addition, it can pose serious problems for patients who have diabetes or peripheral vascular disease. The infection causes discolouration, thickening and crumbling of the nails. It is usually caused by the same organism that causes athlete's foot and ringworm.Toenails are most commonly affected, but it can also occasionally be found in fingernails. The condition is more common where the nails have been damaged and in people with long-standing athlete's foot.
The infection starts at the exposed end of the nail when the infecting organisms get under the nail plate (the hard part of the nail). As the infection spreads, the whole of the nail bed becomes involved and the full thickness of the nail plate is affected too. And unfortunately, the infection does not go away on its own. Ideally, a suspected fungal toenail infection should be confirmed by microscopic examination of nail clippings and scrapings from underneath the affected nail(s). However, if only one or two nails are affected, it is worth trying a topical treatment.
There are two important points to remember when treating fungal toenail infections. First, the infection is deep in the nail bed and the main difficulty is getting an antifungal agent to the site of action (i.e. through the nail). An important step in most treatments is reducing the thickness of the nail to improve penetration. This is done by filing across the nail €“ and then discarding the used file to avoid infecting other nails. Some products come with disposable files for this purpose. Second, toenails grow slowly and so treatment €“ filing down and applying the product €“ usually needs to continue for six to 12 months. There is no such thing as an instant cure for a fungal nail infection. When a treatment is effective, the new healthy nail starts to grow from the base and eventually the infected nail grows out.
There are two types of OTC medicines for fungal nail infections €“ antifungal nail paint and chemical removal of the nail followed by a topical antifungal agent. Antifungal nail paints contain specific antifungal agents such as amorolfine (OTC), tioconazole and ciclopirox (both prescription). Chemical removal of the infected parts of the nail can be achieved using a high concentration of urea. There is an OTC product available which contains 40 per cent urea ointment, waterproof toe plasters and a scraper to remove the softened parts of the nail. Once the damaged parts have been removed, antifungal paint or cream can be applied.
Other products for the treatment of fungal nail infections create an acidic environment that is believed to be hostile to the growth of fungi, or general antiseptics such as benzalkonium chloride.Treatments are relatively expensive and time-consuming. Helping patients to choose a product that is most likely to be effective is therefore an important task.
