1. When breast milk isn't an option
In 0-6 months
Follow this topic
Bookmark
Record learning outcomes
When breast milk isn’t an option and cows’ milk isn’t suitable, infant formula milk is the only accepted substitute for babies aged 0-6 months
Breast milk is the gold standard for babies up to six months of age, but infant formula milk does have an important role to play when a mother cannot or chooses not to breastfeed or to rely on breastfeeding entirely. Cows’ milk as a drink is not recommended for babies under 12 months, so infant formula milk is the only accepted substitute for breast milk. Infant formula milk is based on cows’ milk, but has been modified to make it nutritionally appropriate.
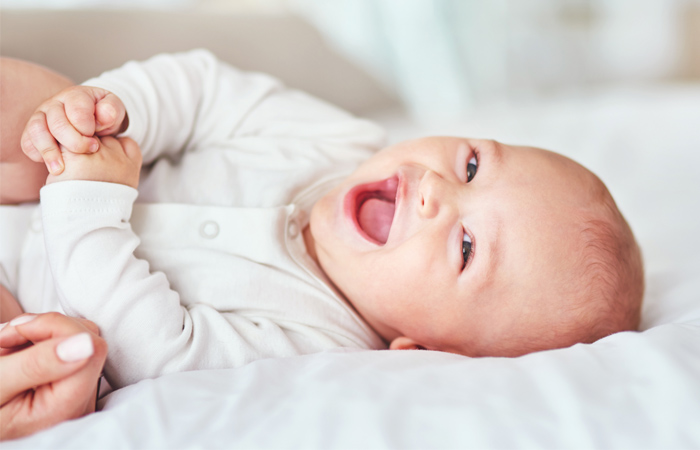

Modifications include:
- Altering the whey:casein ratio to be closer to mature breast milk. N.B. this will be different in milks for hungrier babies
- Increasing the lactose content by altering the carbohydrate concentration
- Removing the fat from cows’ milk and adding vegetable oils to increase the absorption of essential fatty acids
- Reducing the sodium (salt) content as this is too high in cows’ milk for an infant’s immature kidney function
- Adding vitamins, minerals and other key ingredients (e.g. nucleotides, alpha-lactalbumin, long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (LCPs) and oligosaccharides such as FOS and GOS).
Whole goat milk formula is also available as an alternative to cows’ milk formula, following the European Food Standards Agency (EFSA) scientific opinion. This concluded that the growth and nutritional outcomes provided by whole goat milk formula did not differ from those provided by a standard whey-based cows’ milk formula. This led to an amendment of the infant formula and follow on formula regulations.
Goat milk formula has a secretion process and casein profile similar to breast milk; is based on whole milk so is less processed and is easily digested, and there is no need to add whey proteins.
It may be used as an alternative for babies with minor feeding issues who are not settling on cows’ milk formula, but it is not suitable for cows’ milk protein allergy, unless directed by a healthcare professional.
Even today, we are still unable to replicate certain substances found in breast milk (e.g. hormones, antibodies and enzymes), but research continues to try to identify their role in the hope that they can be included in all infant formula milks.
Babies undergo a rapid growth phase during the first six months of life
Appetite
Babies are not all the same and appetites will vary even among those of the same weight or age. A baby’s appetite will also vary from day to day and week to week. Advise parents to let their babies be the guide as to how hungry they are by looking out for these signs:
- When the baby has had enough, they will fall asleep or let go of the teat
- If a baby doesn’t want to finish a feed, don’t force them
- If they are still awake and interested in the bottle when the feed is finished, they probably need larger feeds.
Winding after feeding
Some babies are not troubled by wind, while others suffer after every feed. The aim of winding babies is to remove air from their stomachs because air can make them uncomfortable and stop them settling. Babies can swallow air when they drink, especially from a bottle, and when they cry. In general, babies need to be winded halfway through a feed and when they have finished.
There are two main positions for winding:
- Lying the baby over a shoulder
- Sitting the baby on a lap, holding the back and chin.
The baby’s back should be rubbed or patted until they bring up their wind – often with a satisfying burp! Some babies bring up a little milk or ‘posset’ during winding, so it can be useful to have a cloth or muslin square handy.
 The Healthy Start scheme
The Healthy Start scheme
Healthy Start is a Government scheme that provides weekly vouchers to eligible parents with children up to four years of age for infant formula milk suitable for babies from birth, cows’ milk, or fresh or frozen fruit and vegetables. Follow-on milk, soya formula and ready-made weaning foods are not included in the scheme. All pregnant women under 18 years of age qualify, along with pregnant women or families with children under the age of four who are on certain benefits. Further information can be found at Healthy Start.
