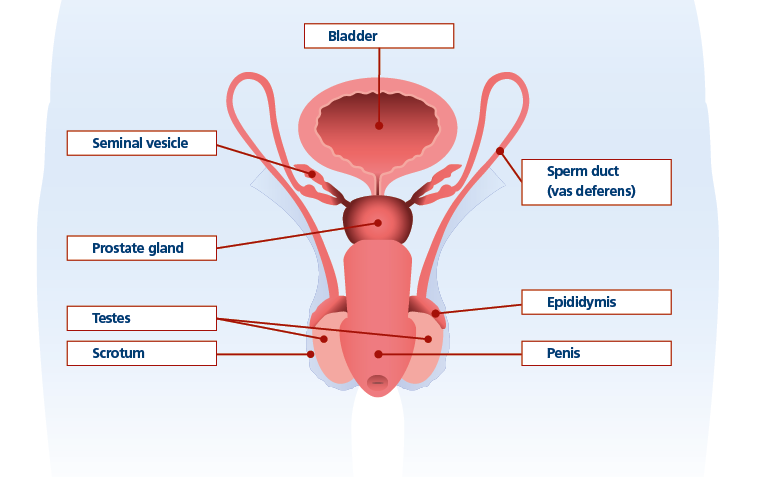
The testes secrete the male sex hormone testosterone, as well as the male sex cells, which are called sperm. The process by which sperm is produced is known as spermatogenesis and takes around two months. Once formed, sperm cells are stored in the epididymis – a tube close to the testes. Both the testes and epididymis are housed in the scrotum. This is a sac that hangs outside the body in order to maintain the slightly lower than body temperature needed for spermatogenesis; there are several other factors that influence this process including testosterone levels and nutrition.
The sperm duct (also known as the vas deferens) extends from the epididymis and transports sperm to outside the body. There are two structures which assist: the seminal vesicle secretes fluid that helps transport sperm and provides nutrients to keep the cells active, and the prostate gland which also produces liquid and other substances to ensure sperm survive. The combination of these liquids plus sperm is known as semen.
As the sperm duct continues towards the outside of the body, it passes through the ejaculatory duct and into the urethra. The urethra also transports urine, but during intercourse, the exit from the bladder is blocked so only semen flows through. The urethra runs through the penis, which consists of erectile tissue that when filled with blood, becomes firm to enable sexual intercourse.
Ejaculation results from rhythmic contractions of smooth muscle in the sperm duct and contraction of the seminal vesicle and prostate gland. The nervous system plays a significant part in this process.
Male puberty
The male reproductive system also matures during puberty – a process that takes approximately six years and starts around the age of 12 when the production of testosterone rises. This process also causes a number of changes, both physical (increased bone and muscle mass and height, hair growth on body and face, deepening of the voice, growth of sex organs) and behavioural (improved self-control; skills in planning, problem-solving, decision-making).
