Contact dermatitis
Contact dermatitis is a type of eczema. It commonly affects the hands and causes red, itchy and scaly skin. In severe cases, the skin can become blistered, very dry and cracked.
This inflammatory skin condition occurs when a sufferer comes into contact with a particular substance. This could be an irritant that affects the skin on contact (irritant contact dermatitis), or an allergen that affects the skin via the immune system (allergic contact dermatitis).
Knowing their triggers can help sufferers to avoid flare-ups, while the regular use of emollients can soothe irritated skin. Corticosteroid creams can be applied to treat severe symptoms.
Psoriasis
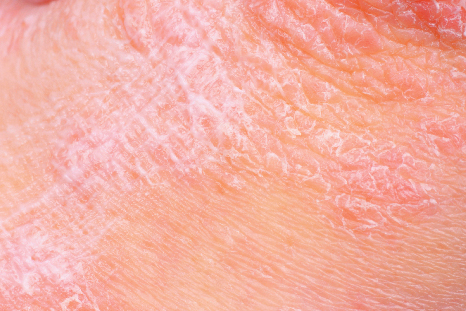 Psoriasis affects up to two per cent of people. Symptoms include red, flaky patches of skin covered with silvery scales. Sufferers can experience periods of mild or no symptoms, followed by periods when symptoms are more severe.
Psoriasis affects up to two per cent of people. Symptoms include red, flaky patches of skin covered with silvery scales. Sufferers can experience periods of mild or no symptoms, followed by periods when symptoms are more severe.
The condition is caused when the process of producing skin cells is accelerated. This creates a build up of cells on the skin's surface. Why this happens is not fully understood, but it may be related to the immune system.
Although there is no cure for psoriasis, a range of treatments including topical creams, gels, and ointments (e.g. vitamin D analogues) are usually recommended. Phototherapy and systemic treatments may be recommended depending on the condition's severity.
It is best to refer customers with psoriasis to the pharmacist, because although some OTC treatments are available, others may require a prescription from a GP.
