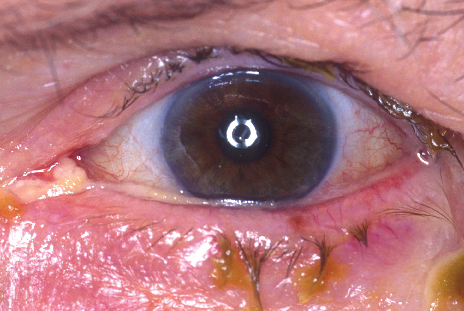
Infective conjunctivitis is inflammation of the conjunctiva, which is the thin membrane covering the whites of the eyes and the insides of the eyelids. It has a number of causes. It can be caused by a virus or bacteria and is very contagious.
What are the symptoms?
The infection usually starts in one eye and quickly spreads to the other. It can also easily spread from one person to another. The whites of the eyes look pink and the eyelids can become red and swollen. There may be a sticky discharge so that the eyelashes stick together on waking and the eyes may feel gritty or irritated.
What are the treatment options?
Eye drops and ointments containing chloramphenicol are available OTC to treat acute bacterial conjunctivitis. They can be used together €“ e.g. the drops can be used in the daytime and the ointment at night. Examples: Optrex Infected Eyes Eye Drops (0.5% chloramphenicol), Brochlor Eye Ointment (1% chloramphenicol).
Chloramphenicol is an antibiotic that can be used from two years of age. As with any antibiotic, completing the course is important. Chloramphenicol products should be used for five days; after this, they should be discarded. The eye drops should be stored in a fridge.
Another treatment option is propamidine isethionate. Example: Brolene Eye Drops.
